
Lean Six Sigma works for small, medium (SMBs) and large businesses. In fact, often times, the same success that is achieved within large businesses can be achieved in small and medium businesses since smaller organizations can move faster because fewer people, fewer resources and lower levels of red-tape are involved.
The benefits are boundless, as Lean Six Sigma increases revenue and reduces costs, while freeing up resources that can be utilized toward any endeavor your organization wishes to pursue.
For example:
- A new product or service
- Other improvement projects
- Expanding your sales force
Lean Six Sigma not only increases revenue and reduces costs, it positively affects people by engaging them in improving the way they work. Since employees are the closest to the actual work (production of a product or delivery of a service) of any organization, they become the best resources to understand how to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes.
By participating in successful Lean Six Sigma projects, employees are able to build the confidence and develop the capability to become your business’ most important assets. Studies show that when employees feel that they have a positive effect the organization, they perform better, are more accountable and live happier lives. And once your employees get comfortable with Lean Six Sigma skills, they can continue to find and remove problems and waste in your organization.
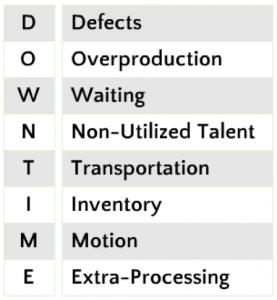
- Defects – Products or services that are out of specification that require resources to correct.
- Overproduction – Producing too much of a product before it is ready to be sold.
- Waiting – Waiting for the previous step in the process to complete.
- Non-Utilized Talent – Employees that are not effectively engaged in the process.
- Transportation – Transporting items or information that is not required to perform the process from one location to another.
- Inventory – Inventory or information that is sitting idle (not being processed).
- Motion – People, information or equipment making unnecessary motion due to workspace layout, ergonomic issues or searching for misplaced items.
- Extra Processing – Performing any activity that is not necessary to produce a functioning product or service.
To remember the 8 Wastes, you can use the acronym, “DOWNTIME.”

